Blending probiotics and prebiotics to lose:

Blending probiotics and prebiotics to lose weight effectively
Blending probiotics and prebiotics to lose: Having a leaner weight during summer
Probiotics are live bacteria in yogurt, other dairy products, and pills. Even though probiotics have shown effectiveness in managing certain gastrointestinal conditions, they do not have the same power that prebiotics do. They’re delicate, heat and stomach acid can easily kill them rendering them ineffective even before they are digested. Again, those who don’t eat dairy foods for taste or dietary reasons may find ingesting adequate amounts of probiotics difficult, if not impossible. Prebiotic is a specialized plant fiber that beneficially nourishes the good bacteria already in the large bowel or colon. The body itself does not digest these plant fibers; instead, the fibers act as a fertilizer to promote the growth of many of the good bacteria in the gut. These, in turn, provide many digestive and general health benefits. Therefore, blending probiotics and prebiotics is essential in losing weight says doctor Dalal Akoury MD President and founder of AWAREmed health and wellness resource center.
Blending probiotics and prebiotics to lose: Probiotics and Children
Probiotics are generally safe for children; however, you should speak with your pediatrician before giving them to your kids. They may be beneficial for digestive complaints and diarrhea, but research hasn’t clearly indicated any benefits beyond that. They are live microorganisms found in particular foods that help promote good gut health. Consuming probiotics is thought to increase the “good” bacteria within your gut and assist in maintaining an optimal balance between the good and the bad bacteria that are present.”
According to one published in Bravo 2011, it was established that mice that were fed on a particular strain of probiotics showed significantly fewer stress levels, anxiety and depression-related behaviors than those who were not given any probiotics. Besides, they also had lower levels of the stress-induced hormone corticosterone. That means, if you want to lower stress and boost your gut health, with probiotics, then you will need to try foods rich in probiotics like yogurt with live active cultures, kefir buttermilk, some blue and aged cheeses, as well as non-dairy products such as fermented foods and soy sauce.
The process of manufacturing the food can kill the probiotics strains, which help in improving your gut health, thus, it is important to look out for words like “live” “active” “raw” “unheated” or “unpasteurized”, if you are planning to buy commercial brands from the market. If you don’t like market products, you can make your own gut boosting products at home yourself, by utilizing simple processes.
On the other hand, Prebiotics are non-digestible, or selectively digestible, carbohydrates that fuel the growth of healthy bacteria in your gut. For this reason, consuming both, foods rich in probiotics, as well as those rich in prebiotics, can be beneficial to your gut health. Many prebiotics is soluble fibers that are fermented by the bacteria in your gut to produce short chain, fatty acids, which have a range of beneficial effects on your body. These short chain fatty acids are known to reduce inflammation and play a role in digestive health and reduce the incidence of bowel cancer. This is what we champion for as experts from AWAREmed health center and for all your weight loss concerns, you can schedule an appointment with us today and will help you professionally.
Blending probiotics and prebiotics to lose: Having a leaner weight during summer
http://www.awaremednetwork.com/


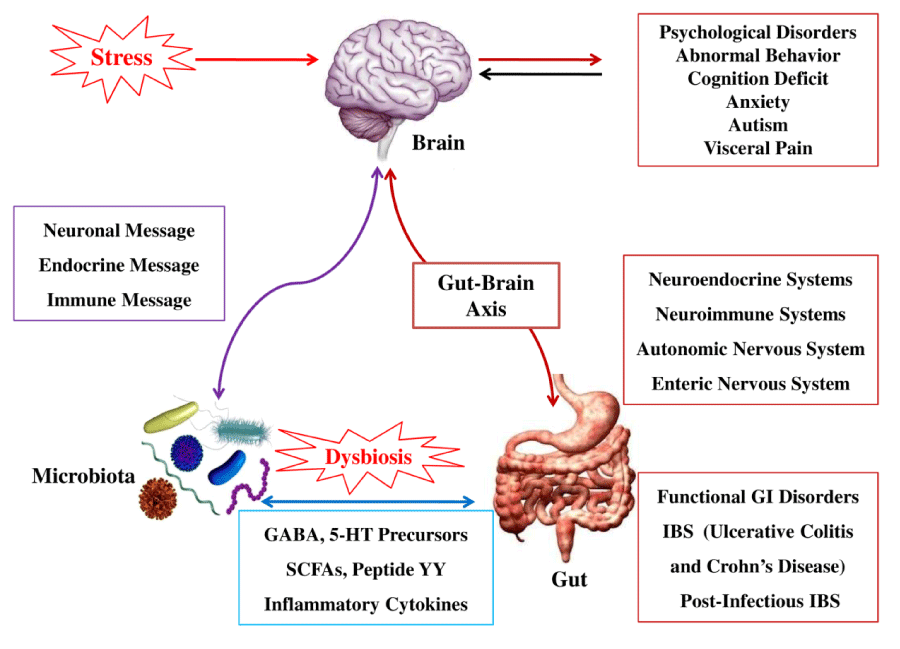
 An exciting new concept is emerging in health and disease is the capability of microbiota in the gut to establish communication with the human brain and alter its behaviour. This can introduce a new arena, that when people make decisions, whether they are influenced by the microbiota of their gut or not. The bidirectional communication between the brain and the gastrointestinal tract is essential for keeping homeostasis. This signalling is regulated at hormonal, neural (both enteric and central nervous systems) and immunological levels. Disturbing these systems leads to
An exciting new concept is emerging in health and disease is the capability of microbiota in the gut to establish communication with the human brain and alter its behaviour. This can introduce a new arena, that when people make decisions, whether they are influenced by the microbiota of their gut or not. The bidirectional communication between the brain and the gastrointestinal tract is essential for keeping homeostasis. This signalling is regulated at hormonal, neural (both enteric and central nervous systems) and immunological levels. Disturbing these systems leads to