Exploring drug addiction causes

Exploring drug addiction causes was not embraced by our great grandparents and so the effects right now are in the brain.Neurochemical reward and drug addiction effects on the brain may include certain pleasurable principle and that explains why the brain needs to be protected the most
Exploring drug addiction causes: The nutrition way
It is almost becoming common knowledge that alcohols among other substances are the commonly abused drugs not just in your state, but across the globe. Because of this, many lives are lost in the process and so we all need to pool together to educate our young ones on the dangers of substance abuse by way of exploring drug addiction causes and effective solutions. With the knowledge of this common factor, it is equally important to appreciate that what may not be common in the public knowledge is the possible roots and genesis of drug taking and drug addiction. This is what we want to address in this article as we progress into the discussion. In our last article, we introduced the causes sighting poor diet and the brains consequent magnetic and chemical imbalance as some of the primary root causes of drug taking and drug addiction. Progressively, we want to engage the expertise of professionals from AWAREmed health and wellness resource center under the leadership of doctor Dalal Akoury MD by way of exploring drug addiction causes. And in doing so, our focus is going to be on the deficiency of nutrients as we progressed into the discussion.
Exploring drug addiction causes: Serotonin
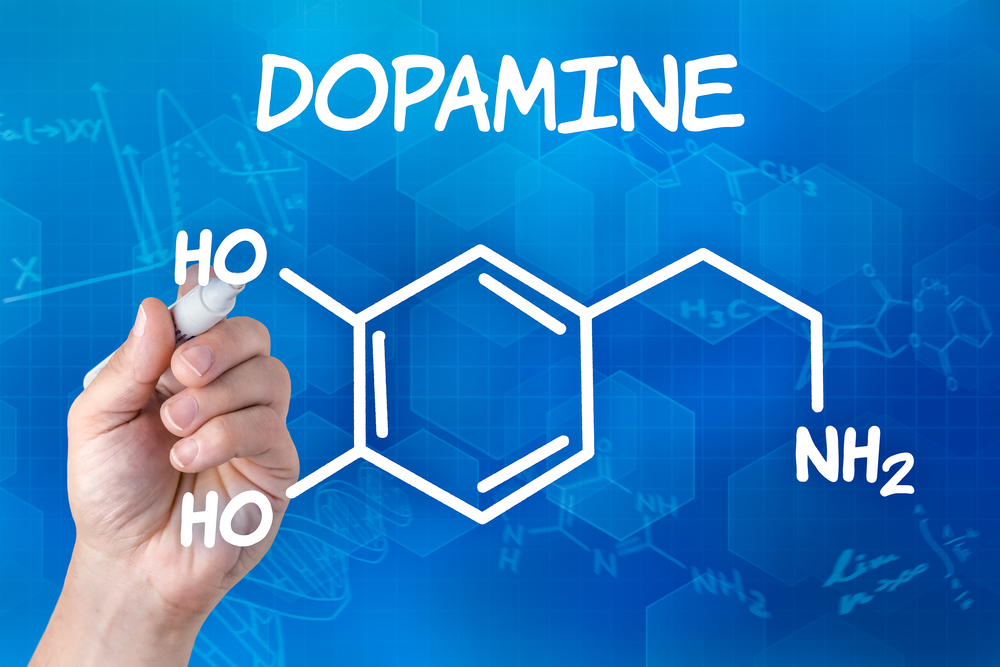
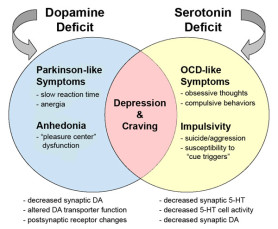
Diet is the key to the synthesis of the neurotransmitter serotonin which has been linked to drug taking. The dietary precursor for serotonin is the amino acid tryptophan which is low in the high-protein diet and high in a high-carbohydrate diet. The effects of drug taking may either increase or decrease levels of serotonin in the brain depending on the patient taking the drug. Individuals responds differently where in some people, alcohol increases their serotonin levels, possibly by decreasing levels of other competing amino acids in the blood as they reach the blood-brain barrier, causing them to relax. While other people may find alcohol and sugar decrease serotonin in the brain causing depression or aggression. And in fact, many criminals, as well as those struggling with chronic depression have been found with this condition.
Exploring drug addiction causes: Poor diet and deficiency of serotonin
Poor carbohydrates (sugar) with high protein (meat) are possible elements of abnormal low serotonin levels. The increase in meat and sugar and other refined carbohydrates consumption like junk food over the last two decades may have resulted in generally low brain serotonin levels which may explain the recent epidemic of childhood depression in our society today. Serotonin deficiency has also been linked by researchers to various state of mental illness, drug-taking, and violent crime.
Tryptophan, the precursor of serotonin (5HT), is believed to be a controlling factor in the CNS, affecting the people’s moods, aggression, pain, anxiety, sleep, memory, eating behavior, addictive behavior, temperature, endocrine and motor regulation. Abnormalities of 5HT include Parkinson’s disease, MS, sleep disorders Huntington’s, schizophrenia, mania, depression, hypersexuality, bulimia, and much more.
Deficiency of tryptophan and tyrosine, the precursors of serotonergic and catecholamine systems have been found in eight adolescents with impulsive behavior. Thirteen studies of serotonin in aggressive cases have been reported with all showing the concentration of 5-HIAA as cerebrospinal fluid are inversely related to aggression, irritability, hostility and criminal activity, further explaining why seeking for professional input from doctor Akoury from time to time is very important not just for you, but to the entire family.
Exploring drug addiction causes: The nutrition way
http://www.integrativeaddictionconference.com/wp-admin