Neurotransmitter role in drug addiction

Neurotransmitter role in drug addiction includes the treatment of cancer related pain
Neurotransmitter role in drug addiction: Risk and reward that trigger for the release of dopamine
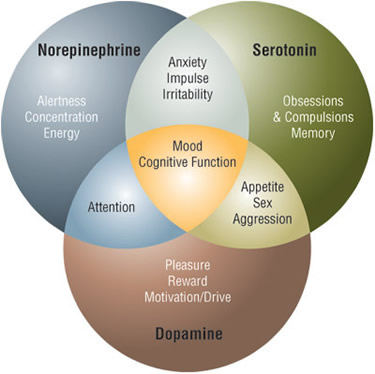
Dopamine is neurotransmitter in the brain that plays vital roles in a variety of different behaviors. The major behaviors dopamine affects are movement, cognition, pleasure, and motivation. Dopamine is an essential component of the basal ganglia motor loop, as well as the neurotransmitter responsible for controlling the exchange of information from one brain area to another. However, it is the role that dopamine plays in pleasure and motivation that attracts the most neurobiologists attention. And that is why our discussion is focusing on dopamine the neurotransmitter role in drug addiction in this article. We would appreciate if you can stay with us on the link so that together we can learn and take action where necessary in order to defeat addiction. Nonetheless for a better understanding of this topic, we are going to be relying on the expert opinion of doctor Dalal Akoury (MD) who is also the founder of AWAREmed Health and Wellness Resource Center. This is a facility that she founded primarily to make a difference in the life of people who are suffering from the various forms of drug addiction which is very rampant in the current societies we live in.
For better understanding of this point doctor Dalal Akoury says that in certain areas of the brain when dopamine is released it gives one the feeling of pleasure or satisfaction. These feelings of satisfaction become desired, and the person will grow a desire for the satisfaction. To satisfy that desire the person will repeat behaviors that cause the release of dopamine. For example food and sex release dopamine. That is why people want food even though their body does not need it and why people sometimes need sex. These two behaviors scientifically make sense since the body needs food to survive, and humans need to have sex to allow the race to survive. However, other, less natural behaviors have the same effect on one’s dopamine levels, and at times can even be more powerful. Often these behaviors can result in addiction due to their effect on dopamine, and that addiction can have negative effects on a person’s well-being.
Neurotransmitter role in drug addiction: Cocaine
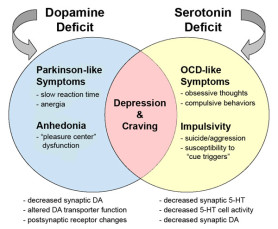
Cocaine is by far more severe in relation to other substances in terms of addiction. Cocaine chemically inhibits the natural dopamine cycle. Normally, after dopamine is released, it is recycled back into a dopamine transmitting neuron. However, cocaine binds to the dopamine, and does not allow it to be recycled. Thus there is a buildup of dopamine, and it floods certain neural areas. The flood ends after about 30 minutes, and the person is left yearning to feel as he or she once did. That is how the addiction begins and with time adaptation builds up due to the fact that the person is consistently behaving in the same way that he or she had the first time. However, the individual cannot, because dopamine is also released when something pleasurable yet unexpected occurs. During the first time, the person expects the effect, thus less dopamine is released, and the experience is less satisfying. This cause explains why gambling releases dopamine.
Many studies have been done which targeted neural response to rewards. The findings were in agreement that when one performed an action repeatedly, and is given a reward randomly, the dopamine levels rises. If the reward is administered for example every four times the action was performed, the dopamine levels remained constant. Whereas when no reward is given dopamine levels dropped. These random rewards can be seen in gambling and since the outcome is based on chance, one may not know prior if he or she will win. Therefore, if he or she wins, dopamine levels increases. However, unlike cocaine, gambling causes addiction in relatively low levels of participants. This is because Cocaine’s chemical input is much more influential on dopamine levels than gambling’s behavioral input meaning that only people whose dopamine levels are low, become addicted to gambling. This may sound technical and complicated, but a phone call to doctor Dalal Akoury will make it much easier for you if only you can schedule for that appointment today.
Neurotransmitter role in drug addiction: Risk and reward that trigger for the release of dopamine
http://regenerativepotential.com/wp-admin