Neurochemical grounds

Neurochemical grounds of addiction. W have a solution for you at AWAREmed health center
Neurochemical grounds of addiction: The exhausted GABA
In order to understand the neurochemical grounds of addiction, it is important that we first understand how GABA operates. And to do so, we are going to speaking to doctor Dalal Akoury MD, President, and founder of the AWAREmed health and wellness resource center. And the submission she brakes the understanding as follows.
- The neurons
- The central nervous system (CNS)
- Inhibitory neurotransmitters
- Excitatory neurotransmitters
Having discussed the first two previously, we are going to progress with the remaining as follows:
Neurochemical grounds of addiction: Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
- Some neurotransmitters act like a brake on a car.
- They inhibit or slow down the actions of the neurons.
- These are called inhibitory neurotransmitters.
- Other neurotransmitters act like an accelerator.
- They increase the speed of the actions of the neurons. These are called excitatory neurotransmitters.
- GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain.
Neurochemical grounds of addiction: Excitatory Neurotransmitters
- Excitatory neurotransmitters are vital to:
- Help us stay alerted
- Maintain our normal memory functions
- Maintain our co-ordination
- Maintain normal emotional responses
- Maintain our heart rate
- Maintain our blood pressure
- Glutamate (a common amino acid) is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain.
Which neurotransmitters are released?
- If there is something that creates:
- Anxiety
- A feeling of panic
- Other stress
- Excitatory neurotransmitters are released and a person can feel:
- Restlessness
- Higher than normal irritability
- Rapid heartbeats
- High blood pressure
- Insomnia
- Even seizures.
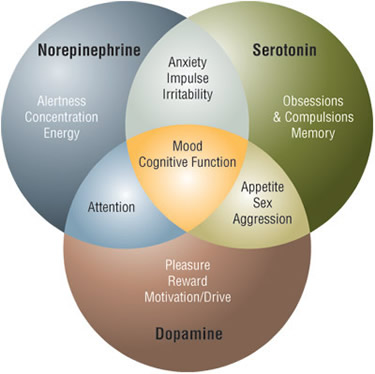
The role of GABA in the brain
- Glutamate speeds things up and when they are going too fast, GABA slows them back down.
- If there is a problem with the GABA in our brains, the neurons fire more and more, increasing the speed of the processes in the brain?
Neurochemical grounds of addiction: How GABA works
When GABA binds to a nerve cell receptor, it opens the nerve cell so that chloride ions present in the brain are allowed to move into the nerve cell to slow the activity of the cell, and the person normally experiences a calming feeling. For example, if our brain produces more excitatory neurotransmitters like norepinephrine or epinephrine (adrenaline) than normal, we can become anxious or have more stress than normal. And when the brain is working normally, it will produce more GABA thereby slowing down the actions in the brain and thus have a calming and relaxing effect on us.
Finally, this article will go a long way in helping you do the right thing with your life. In doing so certain professional decisions will have to be made and to do this, seeking for the expert opinion will be necessary. And that is where doctor Dalal Akoury and her team of experts come in. the lever of professionalism at this facility (AWAREmed health center) speaks for itself since doctor Akoury’s practice focuses on personalized medicine through healthy lifestyle choices that deal with primary prevention and underlying causes instead of patching up symptoms. This is what you need and calling her on telephone number 843 213 1480 should be your starting point for the total life transformation.
Neurochemical grounds of addiction: The exhausted GABA