Chronic inflammation effects on human organs

Chronic inflammation effects on human organs, seek solution from the experts
Chronic inflammation effects on human organs: The damage caused by inflammation
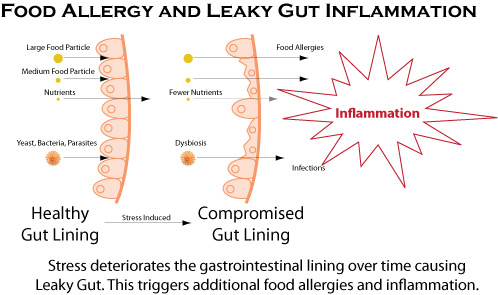
Some of the health conditions affecting our life are known to us yet we often don’t notice them easily. Take for instance all the problem that are associated with chronic inflammation effects; many of us do not take notice of this until we experience an injury either by way of swellings, redness and pain flood that affects the area. But even with this indication, when we opted for treatment our focus is always on the pain and not the internal healing process. Inflammation can damage organs and cause disease, but its interference in the brain causes two common disorders. We are therefore going to be discussing the effects of inflammation on the body organs for better understanding of the body’s vulnerability to this complication. Doctor Dalal Akoury explains that ordinarily your body’s defense mechanism kicks in, and you don’t have to think too much about inflammation because it is always there when you need it.
However even though this is so, inflammation might also occur when you don’t need it, and if it does, it can cause problems. In some people, inflammation is present at very low levels. It is no wonder that many experts now believe that this type of low-grade, chronic inflammation is responsible for a litany of chronic conditions. And according to the experts from AWAREmed Health and wellness Resource Center under the able leadership of doctor Dalal Akoury MD, when inflammation extents to the pancreas the affected person is at risk of getting diabetes. When it spreads to the immune system, you get cancer. And like cancer, this type of inflammation grows and spreads, damaging organs and causing all kinds of trouble. We will be focusing on this for a while but in the meantime, if you have any concern about this problem, doctor Akoury is always available for you and will help you in the best and professional manner.
Chronic inflammation effects on human organs: Weakened signals
The speed with which inflammation spreads does not only cause damages to your organs, but also interferes with your brain’s signals and to the rest of your body systems. With such many conditions the trouble starts in the hypothalamus which is the command center of the brain. The command center then receives all these hormonal inputs that inform you when you’re tired or when to eat and what to do with those calories.
When you have inflammation, a protein called pro-inflammatory cytokines distorts those hormonal signals. As a result, inflammation might be causing conditions such as depression and obesity, which were correlated through research long before inflammation became a suspected culprit. Nonetheless when it comes to depression, those cytokines communicate with the brain to induce different depressive symptoms, such as sad mood, fatigue, altered sleep and social-behavioral withdrawal. Inflammation also drives obesity in a similar manner.
Chronic inflammation effects on human organs: The damage caused by inflammation