Effects of Inflammation on cancer patients
Effects of Inflammation on cancer patients: The Importance of diet and good nutrition
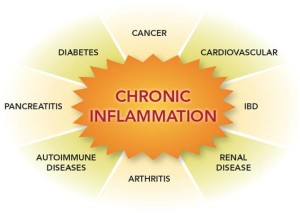
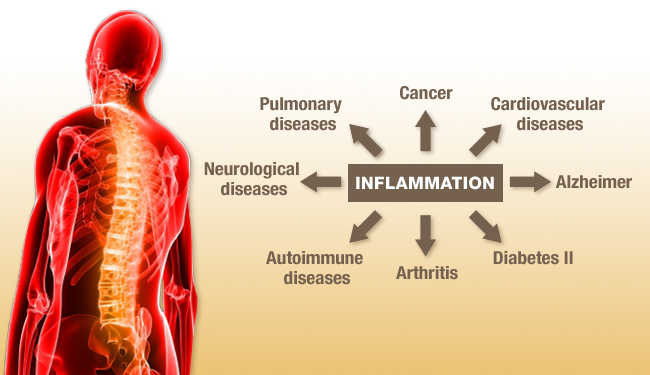
The meaning of inflammation can be understood in two different ways depending on how it affects the body. Like for instance inflammation could be defined as a localized physical condition in which part of the body becomes reddened, swollen, hot, and often painful, especially as a reaction to injury or infection. It could also be defined as the body’s attempt at self-protection; the aim being to remove harmful stimuli, including damaged cells, irritants, or pathogens – and begin the healing process. What this means is that when anything harmful or irritating affects any part of our bodies, there will be always a biological response to try to remove it. The understanding of that is that the signs and symptoms of inflammation, specifically acute inflammation, show that the body is trying to heal itself. Therefore inflammation does not necessarily mean infection, even when an infection causes inflammation. Infection itself is caused by a bacterium, virus or fungus, while inflammation is the body’s response to it. With that elaborate understanding of what inflammation is, the a million dollar question would be what does it have to do with cancer? In other words what are some of the effects of inflammation on cancer patients? Keep reading and in a little while doctor Dalal Akoury MD and founder of AWAREmed Health and Wellness Resource Center will be giving us the finer details.
The truth of the matter is that irrespective of the definition, prolonged inflammation can cause real damage to your body’s healthy cells and tissue thereby weakening your immune system. It is this state of weakness in the immunity that increases ones risk of contracting the cancer diseases. But like we had indicated, not all inflammation is bad. And the experts say that individuals’ inflammatory response is very essential for the healing to effectively take place. It is this response that signals your body’s immune system to send some white blood cells and chemicals to help in fighting off the infection or repair any injury caused.
Other causes of chronic inflammation may include obesity, smoking, stress, lack of exercise, exposure to secondhand smoke and diet choices. And to make the matter more worse is that chronic inflammation in many cases does not shows no signs. Even though there will be no signs, there is the side which is good. And the good news is you can reduce chronic inflammation and lower your cancer risks. It starts with your diet. An anti-inflammatory diet also can help you avoid diabetes, heart disease and Alzheimer’s. Doctor Dalal Akoury is sharing with us some of the anti-inflammatory diet tips as follows.
Effects of Inflammation on cancer patients: Eat more of plant foods
There is more than you can ever imagine in fresh food products from plants. Did you know that plant foods are the only foods containing anti-inflammatory phytonutrients? Besides that, they are very rich in the antioxidants and fiber your body needs to stay cancer-free. Remember that fiber can also lower levels of C-reactive protein (CRP). CRP is a protein in the blood that signals inflammation. According to the American Institute for Cancer Research, they recommend that when eating, people should consider filling at least two-thirds of their plate with plant foods. Therefore take this guideline seriously and make one half of your plate non-starchy vegetables and/or fruits of all colors. And never forget to make one-quarter of your plate whole grains or starchy vegetables, like potatoes, corn and peas.
Effects of Inflammation on cancer patients: Limit processed foods
Choosing whole, fresh foods and doing your own prep maximizes nutrients and phytonutrients. These nutrients keep us healthy in many ways, while reducing inflammation. Processed foods are lower in nutrients and higher in refined sugars, flours and fats. They’re also usually loaded with artificial ingredients that can increase CRP levels. It is therefore important that you skip highly processed foods, like fast food, packaged and instant foods and steer clear of processed meats, like deli-meats, bacon, sausage, hotdogs and pepperoni. Final avoid taking sodas and sports drinks.
Effects of Inflammation on cancer patients: Balance fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids can help protect your body from chronic inflammation. On the other hand, omega-6 fatty acids increase inflammation.
Many people across the globe are trying to include more omega-3 fatty acids in their diet. But, they’re still eating too much omega-6 fatty acids. The key therefore is balance, so you’ll take in more omega-3 and less omega-6. Also eat foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, tuna, halibut, flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, pecans and avocado. Use oils high in omega-3, such as olive and canola and limit oils high in omega-6, such as corn, sunflower, peanut and soybean. Ensure that when buying your stock get the information of the ingredients on packaged foods. Limit foods made with refined vegetable oils high in omega-6. You’ll find these oils in most snack foods, cookies, crackers and sweets.
Effects of Inflammation on cancer patients: Limit red meat
Eating too much red meat, like pork, beef, lamb, deer and buffalo, can increase your cancer risks. Try to limit red meat to 18 oz. or less each week to keep your cancer risks low. Doctor Akoury suggests replacing red meat with these high protein foods to help reduce chronic inflammation. You can also choose animal proteins, such as skinless chicken, turkey and fish while replacing animal proteins with plant proteins, such as beans and lentils, at some meals. And better still; choose meat, milk, cheese and eggs from pasture-raised and hormone-free animals.
Effects of Inflammation on cancer patients: Eat more fermented foods
Fermented foods such as yogurt, sauerkraut and miso contain probiotics that help reduce inflammation. To get the most health perks, eat at least one small serving of a fermented food each day. Finally at the home of solutions (AWAREmed Health and Wellness Resource Center) there is much more you can get from the most experienced professionals there. For any cancer about cancer and effects of inflammation, you can schedule for an appointment with doctor Dalal Akoury today for further deliberations.
Effects of Inflammation on cancer patients: The Importance of diet and good nutrition