Addictive biochemistry and the HPA axis

Addictive biochemistry and the HPA axis that focuses on the real action points
Addictive biochemistry and the HPA axis: Ending alcohol abuse using alternative treatment
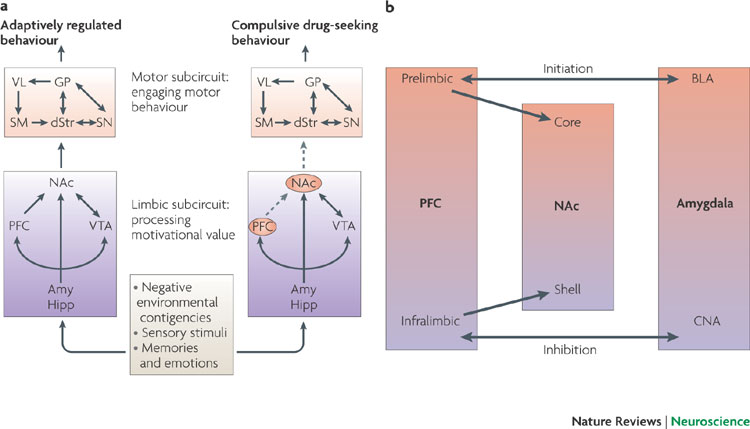
The door to addictive biochemistry opens when either the hypothalamus or one of the organs which serve the hypothalamus in accomplishing this job is injured, or if the nutrients required are not available. In any one of these conditions, the entire system will fall off the “point zero” (homeostasis) that the HPA system tries to maintain opening the door for addictive biochemistry. According to the experts at AWAREmed Health center under the leadership of doctor Dalal Akoury MD, we can’t change the fact that addictive biochemistry and full out alcoholism are associated with overexpression of the sympathetic nervous system; low serotonin, GABA, dopamine, endorphins and enkephalins and it is in the hypothalamus where the delicate job of balancing this network of hormones and neurotransmitters to achieve physical and mental health is supposed to be done whether it be directly from the hypothalamus or via the pituitary and adrenals under the control of the hypothalamus.
Differences between biochemistry and alcoholism
The only difference between addictive biochemistry and full out alcoholism is that addictive biochemistry becomes aggravated, meaning that the deficient condition within the hypothalamus, pituitary or adrenals is made more profound by the damaging effects of alcohol toxicity and the medicating effects which, while drinking, overexpress serotonin, endorphins and dopamine which magnifies the negative impact of an already up-regulated brain chemistry. The symptoms the problem drinker experiences intensify in direct relationship to the diminishing health of the neuroendocrine system which further encourages the person to drink more thus causing further damages. This cycle progressively intensifies until intervention which discontinues and heals the damage is required to stop it.
The pituitary gland is located below the hypothalamus and is directly connected to it via nerve and circulatory pathways. The hypothalamus regulates the function of the pituitary gland which in turn controls hormonal secretions of all other glands; however, specific to alcoholism we are concerned with the function of the adrenals and the secretion of cortisol which is under control of ACTH (adrenocorticotrophin) secreted by the pituitary, and epinephrine and norepinephrine which is also released by the adrenals due to a rise in CRH and/or signals from the sympathetic nervous system. In the case of cortisol release, when the hypothalamus registers low blood sugar it will send CRH (corticotrophin releasing hormone) to the pituitary which then releases ACTH which will cause cortisol to be secreted from the adrenals. This chain of events will also cause the release of epinephrine and to a lesser degree norepinephrine. Prolonged increased levels of epinephrine will block insulin receptors which lead to insulin resistance and lowered serotonin, endorphin, enkephalin and GABA levels which impair HPA functions and increases compulsive/addictive behavior.
The adrenals sit on top of the kidneys and are directly controlled by the pituitary gland. The adrenals are comprised of two sections; one is the medulla which is the inner core and the second is the adrenal cortex which is the outer layer. The medulla relates to the sympathetic nervous system and produces the catecholamine’s epinephrine and norepinephrine. The adrenal cortex produces sex hormones, aldosterone, and what we’re most concerned with cortisol.
Although it is hard to imagine because they are docked on our kidneys, adrenal health is fundamental to our mental health. Proper levels of cortisol, epinephrine and norepinephrine are crucial to our mental well-being so the concentrated focus needs to be applied to their health when healing addictive biochemistry and alcoholism. As you consider breaking way from addictive biochemistry and alcoholism, you can always consult with doctor Dalal Akoury an expert in this discipline for over two decades and has been helping many get their life back globally by emphasizing on Neuroendocrine Restoration (NER) to reinstate normality through realization of the oneness of Spirit, Mind, and Body, Unifying the threesome into ONE.
Addictive biochemistry and the HPA axis: Ending alcohol abuse using alternative treatment
http://www.integrativeaddictionconference.com/wp-admin