Dopamine effects and addiction

Dopamine effects and addiction are very active in the brain malfunctions
Dopamine effects and addiction: The brain
Dopamine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning that when it finds its way to its receptor sites, it blocks the tendency of that neuron to fire. We have noted that it’s associated with reward mechanisms in the brain. That aside, speaking to doctor Dalal Akoury MD, President, and founder of AWAREmed health center, new research on the brain is showing that addiction is a matter of memories, and recovery is a slow process in which the influence of those memories is diminished. That notwithstanding, further studies have also shown that addictive drugs stimulate a reward circuit in the brain. The circuit provides incentives for action by registering the value of important experiences. Rewarding experiences trigger the release of the brain chemical dopamine effects, telling the brain “do it again.” What makes permanent recovery difficult is the drug-induced change that creates lasting memories linking the drug to a pleasurable reward.
Dopamine effects and addiction: Brain circuits
Addiction involves many of the same brain circuits that govern learning and memory. Long-term memories are formed by the activity of brain substances called transcription factors. All perceived rewards, including drugs, increase the concentration of transcription factors. So repeatedly taking drugs can change the brain cells and make the memory of the pleasurable effects very strong. Even after transcription factor levels return to normal, addicts may remain hypersensitive to the drug and the cues that predict its presence. This can heighten the risk of relapse in addicts long after they stop taking the drug.
Knowing more about how addiction works in the brain has not yet given us any effective new treatments, but it has suggested new possibilities while providing a better understanding of how the available treatments work. The hardest job will be finding substances that lower the risk of addiction but do not interfere with responses to natural rewards. So far there is little evidence that any one type of therapy works better for addiction than another.
Dopamine effects and addiction: Brain Chemistry
It has been demonstrated times and again that drug addiction is a powerful force that can take control of the lives of users. In the past, addiction was thought to be a weakness of character or just misbehavior, but in recent decades research has increasingly found that addiction to drugs like cocaine, heroin, and methamphetamine is a matter of brain chemistry.
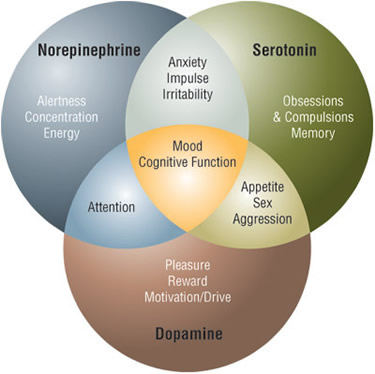
Experts at the National Institute on Drug Abuse, says that the way a brain becomes addicted to a drug is related to how a drug increases levels of the naturally-occurring neurotransmitter dopamine, which modulates the brain’s ability to perceive reward reinforcement. The pleasure sensation that the brain gets when dopamine levels are elevated creates the motivation for us to proactively perform actions that are indispensable to our survival for example eating or procreation. Dopamine is what conditions us to do the things we need to do. Having understood the power of addiction and what it can do to your health, it would be unwise to let drugs bring you down because of ignorance. Doctor Dalal Akoury founded this facility to help you have your life back and live it to the fullest. Waste no time and schedule an appointment with today for the commencement of your recovery process.
Dopamine effects and addiction: The brain