Pleasures registration brain and addiction
Pleasures registration brain and addiction. When drugs get access to the brain, there is bound to be serious health problems
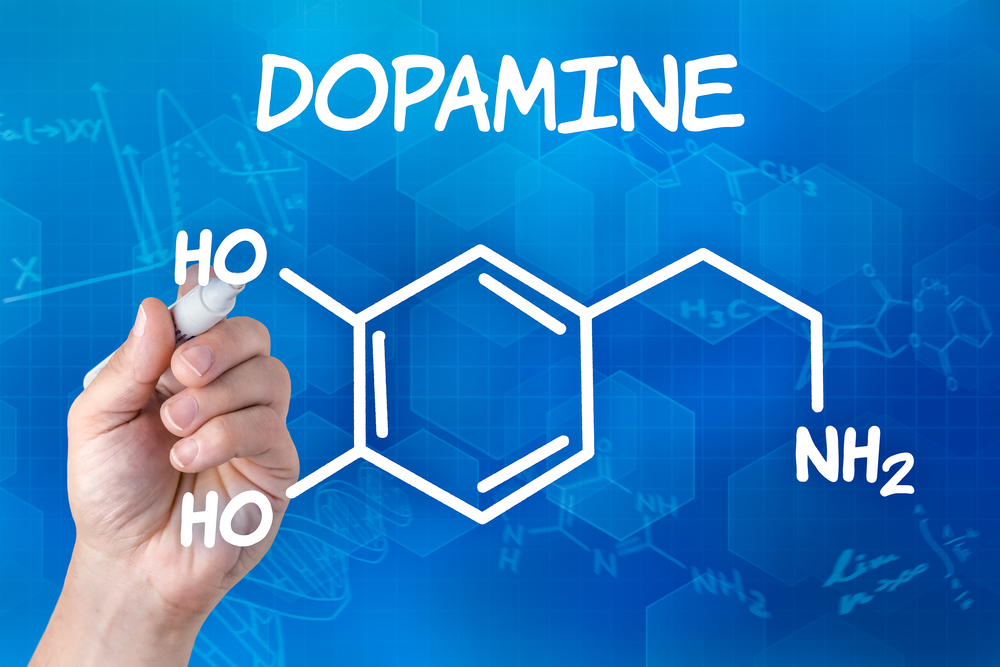
Pleasures registration brain and addiction: Neurotransmitter dopamine
Among the functions of the brain is that of pleasures registration as and when they happen irrespective of their origin. It doesn’t matter whether they’re associated with a psychoactive drug, a monetary reward, a sexual encounter, or a satisfying meal. The fact is in the brain pleasurable principles has a distinct role of releasing the neurotransmitter dopamine in the nucleus accumbens, a cluster of nerve cells lying underneath the cerebral cortex. Dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens is so consistently tied with pleasure that neuroscientists refer to the region as the brain’s pleasure center.
All drugs of abuse, from nicotine to heroin, cause a particularly powerful surge of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens. The likelihood that the use of a drug or participation in a rewarding activity will lead to addiction is directly linked to the speed with which it promotes dopamine release, the intensity of that release, and the reliability of that release. Therefore addictive drugs provide a shortcut to the brain’s reward system by flooding the nucleus accumbens with dopamine. The hippocampus lays down memories of this rapid sense of satisfaction, and the amygdala creates a conditioned response to certain stimuli.
Brain pleasurable principle and drug addiction: Learning the process
Previously it was believed that an experience of pleasure alone was enough to compel people into consistent seeking of addictive elements or activities. However new research findings indicate that the situation may be more complicated. This is because dopamines are not only responsible for the experience of pleasure but are also playing a role in learning and memory which are the two key elements in the transition from liking something to being addicted to it. Currently, the philosophy about addiction is that dopamine interacts with another neurotransmitter, glutamate to take over the brain’s system of reward-related learning. Remember that this system has an important role in sustaining life because it links activities needed for human survival (such as eating and sex) with pleasure and reward.
Finally, it may interest you to note that the reward circuit in the brain may include areas involved with motivation and memory as well as with pleasure. Addictive substances and behaviors stimulate the same circuit and then overload it. And therefore repeated misuse of any addictive substances or behavior will cause nerve cells in the nucleus accumbens and the prefrontal cortex (the area of the brain involved in planning and executing tasks) to communicate in a way that couples liking something with wanting it, in turn driving us to go after it. That is, this process motivates us to take action to seek out the source of pleasure. This can be very unhealthy more so if the source of pleasure is drugs. Many often run to drugs for pleasure and as such, the prevalence of drug abuse is on the rise. We can choose individually and collectively to correct this by scheduling an appointment with doctor Dalal Akoury MD, who is a veteran addiction expert and also the founder of AWAREmed Health and Wellness Resource Center for help today.
Brain pleasurable principle and drug addiction: Neurotransmitter
http://www.integrativeaddictionconference.com/wp-admin