Mitochondrial dysfunction and obesity
Mitochondrial dysfunction and obesity-In action
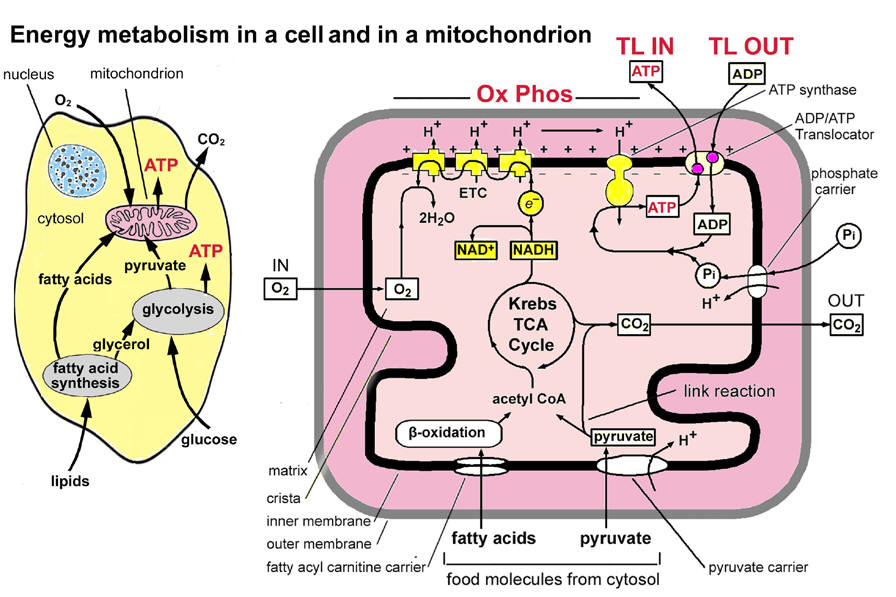
Mitochondrial diseases result from failures of the mitochondria, specialized compartments present in every cell of the body except red blood cells
Dysfunction means that something is not working or functioning in the correct way. Mitochondrial dysfunction refers to a situation in which the mitochondria are not working properly.
Mitochondrial diseases result from failures of the mitochondria, specialized compartments present in every cell of the body except red blood cells. Mitochondria are responsible for creating more than 90% of the energy needed by the body to sustain life and support growth.
When they fail, less and less energy is generated within the cell. Cell injury and even cell death follow. If this process is repeated throughout the body, whole systems begin to fail, and the life of the person in whom this is happening is severely compromised. The disease primarily affects children, but adult onset is becoming more and more common.
Depending on which cells are affected, symptoms may include loss of motor control, muscle weakness and pain, gastro-intestinal disorders and swallowing difficulties, poor growth, cardiac disease, liver disease, diabetes, respiratory complications, seizures, visual/hearing problems, lactic acidosis, developmental delays and susceptibility to infection
Mitochondrial dysfunction -Approaches to Resuscitate Aging Mitochondria
Understanding the proposed mechanisms by which mitochondrial dysfunction can contribute to aging and aging related diseases suggests several potential interventions. These include:
- Maintenance of optimal Krebs cycle and respiratory chain efficiency.
- Restoration of mitochondrial membrane fluidity.
- Reduction in deleterious free radical activity.
CoQ10
Coenzyme Q10 is probably the most widely used cofactor for treating mitochondrial-related diseases. CoQ10 functions as the electron carrier in the inner mitochondrial membrane, transferring electrons from complexes I and II to complex III. In addition to increasing biosynthesis of ATP (the universal energy molecule), and acting as a potent free radical scavenger, CoQ10 also reduces lactic acid levels, improves muscle strength, and decreases muscle fatigability.1
Mitochondrial dysfunction-restoration will cause weight loss
The role of your metabolism is to take the oxygen we breathe and the food we eat and process it to make energy, the fuel for life. (The fuel for your car is called gas. The fuel for your body is called ATP and it is produced from the combustion of food and oxygen.)
When they are not working properly, you suffer all the symptoms of low energy: fatigue, memory loss, pain, rapid aging, and more. Along the way, many things can go wrong that may impede your metabolism, make it run less efficiently, or practically shut it down.
Fatigue is the most common symptom of poorly functioning mitochondria. We need to keep them in top shape. The reason we poop out as we age is the constant insult and injury we give our mitochondria.
We have over 100,000 trillion of these powerhouses in our body, and each one contains 17,000 little assembly lines for making ATP, our major fuel. They use over ninety percent of the oxygen we breathe. They take up forty percent of the space inside the heart cells. The only problem is they are very sensitive to damage.
And the injury is from uncontrolled oxidative stress, which results from toxic insults, infections, allergens, stress, and just eating too much poor quality food.
Dr. Bruce Ames, the renowned scientist from the University of California at Berkeley, has spent the last decade discovering how we can give ourselves a metabolic tune up.
In one study he gave old rats who were tired, wouldn’t get on the treadmill anymore, and couldn’t find the cheese in the maze, or swim very far, two molecules that boost metabolism, that make the mitochondria run better. They are alpha lipoic acid and acetyl-L-carnitine.
Overnight these rats became young rats. They got up on the treadmill themselves, swam long distances without fatiguing and could easily find the cheese in the maze like young healthy rats. How could that happen?
Well, he simply gave the cells the raw materials they need for optimal function. As we age, our metabolism burns out from a lifetime of damage and insults. So again, the way to get healthy, the way to ultra-Wellness is very simple.

Depending on which cells are affected, symptoms may include loss of motor control, muscle weakness and pain, gastrointestinal disorders and swallowing difficulties…
Ultimately the goal of Ultra Wellness is to give everyone a metabolic tune up.
- First, find the things that damage your metabolism and mitochondria.
- Second, give your body the things that help the mitochondria function optimally.
- Getting rid of toxins in the body will give you more energy. So here’s another reason to exercise: Exercise accelerates the detoxification process.
- Exercise pushes the blood to circulate more efficiently through the body, allowing nutrients to move easily to reach all the organs and muscles.
- Exercise helps lymph fluids circulate through the body, which removes toxins and other harmful materials. When you exercise, you naturally take in more oxygen; to make room for the added oxygen, your cells kick out toxins that are taking up space. When you exercise properly, your build up a sweat and toxins are released through the pores of the skin.
- Playing at anaerobic levels is a great way to get in peak shape. It doesn’t do anything for longevity, or probably for overall health, but it’s great for vim, vigor and pure fitness.
- Regular exercise is one of the most important things you can do for health. Participation in physical activity improves several body functions. These include: weight control, decreased risk of cardiovascular disease, decreased risk of diabetes, reduced risk of cancer, improved strength of bones and muscle, enhanced emotional status, decreases the natural degenerative changes that come with aging, and increases your chances to live longer.
- That said, being consistently active can actually cause degeneration. Rest and recovery periods are essential as these periods allow the body to repair and rebuild itself.
Mitochondrial dysfunction –and exercise
It must be noted that consistent exercise can lead to overuse injury. Be sure to discern between consistently exercising and regular exercise.
Mitochondrial dysfunction and obesity-In action
























 Obesity in America: Safe Rapid weight loss, Obesity is preventable
Obesity in America: Safe Rapid weight loss, Obesity is preventable










