Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Inflammation
Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Inflammation modulates Regulatory T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Mesenchymal stem cells are a rare type of cells that are multi-potent and can be isolated from the adipose tissues, bone marrow among other crucial sources. These cells have very unique properties that have seen them become targets of very many medical therapies especially in treating degenerative diseases like aging and even joint diseases like arthritis. These cells have been found to be also very effective in modulating the functions of immune cells, including T cells, B cells, natural killer cells, monocyte or macrophages, dendritic cells, and neutrophils. T cells, activated to perform a range of different effector functions, are the primary mediators of many autoimmune and inflammatory diseases as well as of transplant rejection and graft-versus-host disease. Some of the well-defined T-Cell effector cells include; CD4+ (T helper cell) subsets Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes which are derived from antigen-specific activation of simple CD8+ precursors. In addition, naturally occurring and induced regulatory T cells represent CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell phenotypes that potently suppress effector T cells to prevent autoimmunity, maintain self-tolerance, and limit inflammatory tissue injury. The ability of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to suppress the effector T-Cells and limit inflammation has made them very effective in treating rheumatoid arthritis which is characterized with inflammations around the joints. Typically, many immune-mediated diseases entail an imbalance between regulatory T cells and effector T cells of one or more phenotypes. Mesenchymal Stem Cells broadly suppress T-cell activation and proliferation in a controlled environment outside of a living organism via (Vitro) a plethora of soluble and cell contact-dependent mediators. These mediators may work in two ways; first they can work directly on T cells or indirectly via modulation of antigen-presenting cells and other accessory cells. Mesenchymal Stem Cells administration has also been shown to be variably associated with beneficial effects in autoimmune and transplant models as well as in several human clinical trials. However, in a small number of studies Mesenchymal Stem Cells administration has been found to heighten T cell-mediated tissue injury. The multiple effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on cellular immunity may reflect their diverse influences on the different T-cell effector subpopulations and their capacity to specifically protect or induce regulatory T-cell populations.
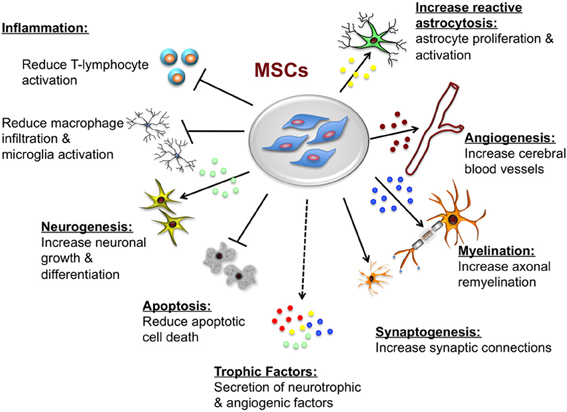
Mesenchymal stem cell modulation of T cell-mediated immune responses
To repeat for emphasis, the T cells are the primary cellular effectors of the adaptive immune system and their functional properties are central to antigen specificity and memory associated with cognate immunity, this therefore means that to a greater extent they are responsible for rejection of implanted cells of varied specificity. Antigen-specific activation and differentiation of naïve T cells result in the generation of a range of T-cell phenotypes that may be defined by the acquisition of characteristic cytokine secretion profiles, cytolytic mechanisms, or counter-regulatory properties.
Following antigen-specific adaptive immune responses, a small proportion of activated T cells persist as memory cells and have the capacity to respond more rapidly and potently to secondary encounters with the same antigen. These memory cells may retain the effector phenotype imprinted upon them during primary activation. When these memory cells are appropriately coordinated and regulated, the diversity of T-cell effector phenotypes allows immune protection against a multitude of pathogenic microorganisms while maintaining self-tolerance and homeostasis. On the other hand, over exuberant pro-inflammatory T-cell responses may lead to auto-immune and allergic diseases, including multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, type 1 diabetes mellitus, and asthma. Therefore it is crucial to have a modulatory strategy on the effector T-cells. Furthermore, life-saving treatments such as allogeneic bone marrow and solid organ transplantation may be complicated by alloantigen-specific T-cell immune responses, resulting in graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) or transplant rejection.
Study finding
 In a research study done at School of Medicine, University of Seville, Seville, Spain by Gonzalez-Rey E, Gonzalez MA, Varela N, O’Valle F, Hernandez-Cortes P, Rico L, Büscher D, and Delgado M it was found that human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells suppressed the antigen-specific response of T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibited the proliferative response and the production of inflammatory cytokines by collagen-activated CD4 and CD8 T cells. On the contrary, the numbers of IL10-producing T cells and monocytes were significantly augmented upon human adipose stem cell treatment. The suppressive activity of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells was cell-to-cell contact dependent and independent. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells also stimulated the generation of FoxP3 protein-expressing CD4 (+) CD25 (+) regulatory T cells, with the capacity to suppress collagen-specific T cell responses. Lastly, human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells down regulated the inflammatory response and the production of matrix-degrading enzymes by synovial cells isolated from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
In a research study done at School of Medicine, University of Seville, Seville, Spain by Gonzalez-Rey E, Gonzalez MA, Varela N, O’Valle F, Hernandez-Cortes P, Rico L, Büscher D, and Delgado M it was found that human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells suppressed the antigen-specific response of T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibited the proliferative response and the production of inflammatory cytokines by collagen-activated CD4 and CD8 T cells. On the contrary, the numbers of IL10-producing T cells and monocytes were significantly augmented upon human adipose stem cell treatment. The suppressive activity of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells was cell-to-cell contact dependent and independent. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells also stimulated the generation of FoxP3 protein-expressing CD4 (+) CD25 (+) regulatory T cells, with the capacity to suppress collagen-specific T cell responses. Lastly, human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells down regulated the inflammatory response and the production of matrix-degrading enzymes by synovial cells isolated from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
The study had sought to find out the immunosuppressive activity of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on collagen-reactive T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The method used involved investigating the effects of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on collagen-reactive RA human T cell proliferation and cytokine production as well as effects on the production of inflammatory mediators by monocytes and fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Stem cell therapy is a promising approach to treatment of degenerative diseases like arthritis but still you will need an expert in degenerative medicine. Dr. Dalal Akoury (MD) an expert in integrative and regenerative medicine will be able to help. Visit us at AWAREmed Health and Wellness Resource Centre at Myrtle Beach, South Carolina




















