Dr. Dalal Akoury
IS DYSBIOSIS and ADDICTION CAUSE OR RESULT ?
Dysbiosis and Addiction, they go hand in hand. Dysbiosis is also referred to as dysbacteriosis in the medical fields. It is referred to as the state of imbalance of intestinal micro flora that is bacteria and other many microorganisms. Dysbiosis is a situation that can lead to excessive bacterial fermentation in the gut of the humans. In many of the cases, it has also been associated with autointoxication more especially from the endotoxins which are produced by the undesirable bacterial effects that occurs within the body. The derived meaning of Dysbiosis is represents “dys” which means difficult and “biosis” which represents a way of living.
Call Dr, Akoury at 843-213-14-80 if you think that your addiction is a result of DYSBIOSIS. The presence of bacteria in the body plays a vital role in the body through a very unique relationship that consists of the various different types of bacterial flora that inhabit mainly the gastro intestinal tracts. The GI has about 300 to 500 different types of microorganisms in the body. Micro flora is also present in the skin, and many of the exposed surfaces such as the mucous membrane, vagina, mouth, nose, ears, eyes, and many more other places in the body.
The presence of the microorganisms can be benign making them beneficial or pathogenic when they are responsible for the different illnesses such as the inflammatory bowel diseases and in some cases fatigue. The beneficial micro flora carries out helpful roles as assisting in the digestion and protection of the body from the penetration of the pathogenic microbes. Competition among the microbes as well is present for both the space and the limited resources within the GI.
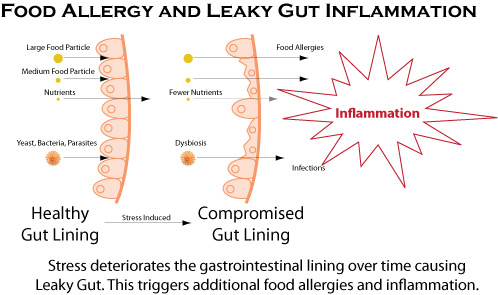
The population of the microbes in the gut can be disrupted by several things such as use of antibiotics, or alcohol or drugs and other substances. The consumption of glucose and dextrose rich food is greatly enhanced their

English: Pathogenomics: Genome Analysis of Pathogenic Microbes (Photo credit: Wikipedia)
leading to their overgrowth of some and disturbance of some of the minute populations.
Dysbiosis Addiction and Alcohol
Alcohol has been established to be one of the most important factors in the cause of liver cirrhosis in many of the industrialized nations in the world. This is associated with many other conditions such as fatty liver also referred to as the steatosis that may progress to alcoholic hepatitis, fibrosis, and later the more advanced cirrhosis. This has a direct impact in the loss of the loss of the liver function and in some cases result in the variceal hemorrhage. Hypotension has also been cited as result of alcoholism, in advanced cases, the live may also develop advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
The most devastating defect during dysbiosis is succumbing to the bacterial infections. This is caused by the translocation which occurs from the passage of the viable bacteria or the products from the small intestines through the epithelial mucosa to the mesenteric lymph nodes, systemic circulation and extra intestinal organs. This is the main pathogenic pathways for the incidence of infections. The hepatocellular infection is also increased with bacterial translocation more especially with the cirrhotic patients and has been cited in the development of the alcoholic liver injury and fibrosis.
Bacterial translocation in many of the cases as well causes severe infection in cirrhotic patients also causes liver injury and fibrosis. Endotoxemia is also very highly common among the patients that are suffering from alcoholic cirrhosis. It is also common in patients that have mild forms of alcohol hepatitis.
Many of the studies in dysbiosis has established that lactic acid have an inhibitory effect on the putrefactive bacteria, the consumption of yoghurt has been stated to be one of the solution to this conditions of autoxidation’s and in the improvement of the composition of the intestinal micro flora in the body.
Theories that address the internal toxemia have also been postulated and have been transformed to the theories of intestinal Dysbiosis that explain the alterations of the populations of the bacteria in the gut. This has also been understood as the factors that influence the qualitative and quantitative changes in the intestinal flora. The changes to a great extent have altered the metabolism of the bacteria; in some cases leading to the overgrowth of the bacteria in the intestine through the release of toxic products leading to the development of chronic and degenerative diseases.
There is much evidence that has been established to prove that disturbances of the concentrations of bacteria plays a role in the myriad of the diseases conditions in the GIT disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease. This has also been associated with the systemic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankolysing spondylitis.
Dysbiosis Addiction, the relationship of Addiction to dysbiosis is very clearly established and leads to severe conditions:
The conditions that lead to Dysbiosis are thus very essential in understanding of the detrimental changes that occurs with micro flora.
The micro flora represents an ecosystem that is very complex. In some of the situations compromises the host health when the micro flora is compromised and drastically altered. The GIT micro flora stimulates the Immune system, synthesizes the Vitamins such as the vitamin B complex and K. It also improves the function and motility of the GIT, promotes digestion processes, absorption of the nutrients, inhibition of the pathogens, metabolism of the drugs and plant compounds, and in the production of the short chain fatty acids and many more poly amine compound in the body.

Cover via Amazon
Alteration of the GIT includes the use of the antibiotics, psychological and physical stress, radiations, altered GIT peristalsis and dietary changes on the body. Alcohol addiction has been established to be a key cause on some of the pathogenic processes associated with Dysbiosis. Alcohol is a main factor in the intestine that lead to the changes in the homeostasis of the intestinal microbial leading to the gastric acid secretion in both the small and large bowel motility
The epithelial cells serve as the main interface between the micro flora and the host individuals. The main function of the epithelial cells includes the secretion of the antimicrobial effector molecules which is part of the mucosal innate immune system. Reg3g is a c-type lectin that has been found to have a key bactericidal activity that is expressed only in the intestinal epithelial cells and paneth cells. The highest levels have been established to be the potent cause of the bactericidal activity. Another type of compound, reg3b has also been mentioned to be responsible for the intestinal homeostasis. The role of excessive alcohol intake addiction has been said to play a significant role in the suppression of the genes and protein expression of the reg3g and reg3b. This adversely contributes to the qualitative and quantitative changes in the enteric flora after alcoholic feeding.
Additional research has been able to show that lowest levels of the Reg3b and reg3g in the proximal small intestines have been associated with the increase in the overgrowth of the bacteria. The restoration of the reg3g is also associated with the declining overgrowth and amelioration of the alcoholic steatohepatitis. This is an indication that there is a link between the alcohol and Dysbiosis.
There is a possibility of the presence of metagenomic, transcriptomics and metabolomics factors in alcoholic livers disease following Dysbiosis. The understanding of the key metabolomics and the transcriptomics will be important in the explanation of the key substrates and mediators of the signaling molecules that will provide a better understanding of the microbe to microbe relationship and the microbe and host relationship. This will possibly be able to provide an idea of the possible manipulation of the specific targeted microorganisms and metabolomics with the help of the dietary supplements, use of the antibiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics.
Dysbiosis Addiction are very closely inter related
Alcohol addiction is therefore greatly associated with the intestinal bacterial overgrowth and enteric and dysbiosis. This is achieved by the dysregulation following the ingestion of the chronic alcohol intake that contributes to the changes in the microbiome and alcoholic steatohepatitis.
It must be noted that the chronic alcoholism is associated with the increase in the concentration of the fats in the body due to the elevation of the levels of HDL and LDL in the body. Putrefaction dysbiosis of created in the body with the diet that is high in fat content and that has a high animal flesh with low content of fat in the diet. This has been associated as the other cause of the Dysbiosis leading to increased concentration of the bacteroides and a decrease in the concentration of the bifidobacteria species more especially in the stool.
Alcohol fermentation also occurs in the GIT as a result of the carbohydrate intolerance that has been induced by overgrowth of the bacteria in the stomach, small intestines and beginning of the large intestines. The changes in the bacterial growth is associates with the decrease in the concentration of hydrochloric acid a condition referred to as hypochlorhydria that induced by long term use of alcohol, it is also associated with the decreased motility of the GIT. The immune deficiency and malnutrition due to the impaired absorption of nutrients in the body as a result of cholestasis and pancreatitis induced in chronic alcoholics. Overgrowth of the bacteria is the only symptom that is a factor in the development of carbohydrate intolerance. This is a defect that is indistinguishable from the intestinal candidiasis as a result of the overgrowth of candida. There are now clear evidence of Dysbiosis such as the development of the anxiety which is a result of the poor intestinal micro flora and that greatly lead to anxiety. It has been proven that low dose of Salmonella toxins induces anxiety in humans.
Another consequence of Dysbiosis is the development of hypoglycemia which is a result of the low blood sugar levels. This leads to the release of adrenaline that brings blood sugar back to rise. In most victims that are susceptible, this can lead to panic attack. The alcohol intake can also lead to the low levels or imbalance in the production of the hormones in the body. The unstable hormone production leads to Dysbiosis. In most cases, addiction causes the thyroid and progesterone hormone to be low while the estrogen hormones to be very high in concentration in the systemic circulation leading to the increase in the release of the epinephrine hormone. The elevation of the epinephrine promotes the development of anxiety. Also, the low thyroid and progesterone levels contribute to the hypoglycemia.
It can therefore be concluded that both causes of addiction are responsible for the changes in the quantities and quality of the micro flora in the body and hence responsible for some of the effects discussed in this study. It is also evident that alcohol addiction through various mechanisms influence dysbiosis through the impairment of the activity of the epithelial cells, and other effects that lead to the development of gastritis, pancreatitis and the reduction in the concentration of the hydrochloric acids. In addition, the addiction to alcohol is associated with the hormonal addiction and hence the effects associated with the Dysbiosis. The results of the Dysbiosis leads to either a high concentration or low number of micro flora which lead to the production of endotoxins in the body that lead to the pathogenesis of other micro flora, while they are also beneficial to the other microorganisms. This is also represented through the symbiotic relationship between the microorganisms and the hosts. In conclusion, both the cause and the results of addiction have an effect to Dysbiosis.
Call Dr, Akoury at 843-213-14-80 if you think that your addiction is a result of DYSBIOSIS.
IS DYSBIOSIS ADDICTION CAUSE OR RESULT ?







 The environment
The environment Another example of microenvironment is that of antimicrobials in the mucosal surfaces of the
Another example of microenvironment is that of antimicrobials in the mucosal surfaces of the